The Vascular Connection: How to Protect Your Heart and Brain

Imagine waking up one morning to find yourself or a loved one struggling to speak, move, or even breathe. The sudden onset of a heart attack or stroke can be a devastating reality for millions of people worldwide. Heart and brain vascular diseases are the leading causes of death and disability globally, yet many of us remain unaware of the risks and warning signs. In this article, we will delve into the world of heart and brain vascular diseases, exploring the causes, prevention strategies, treatment options, and emergency response measures that can mean the difference between life and death. By understanding these critical health issues, we can take the first step towards protecting our most vital organs and living a longer, healthier life.
Understanding Heart and Brain Vascular Diseases
Heart and brain vascular diseases are a group of conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, leading to serious health consequences. According to the World Health Organization ( WHO), cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death globally, accounting for more than 17.9 million deaths per year. In this article, we will delve into the causes of heart and brain vascular diseases, discuss prevention strategies, explore common treatment methods and medications, and provide guidance on emergency response.
Causes of Heart and Brain Vascular Diseases
Heart and brain vascular diseases are often caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. The primary causes include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol levels
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Lack of physical activity
- Unhealthy diet
- Stress
These factors can lead to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, causing them to narrow and harden, which can eventually lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
Prevention of Heart and Brain Vascular Diseases
Preventing heart and brain vascular diseases requires a combination of healthy lifestyle choices and regular medical check-ups. Here are some prevention strategies:
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques such as meditation and yoga
- Get regular check-ups to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar levels
- Eat a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources
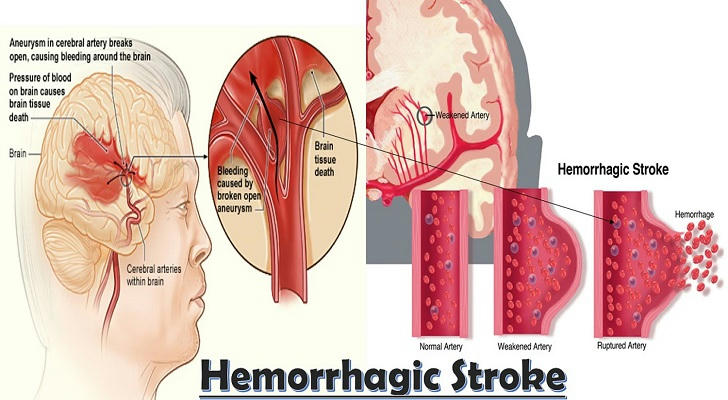
Treatment of Heart and Brain Vascular Diseases
The treatment of heart and brain vascular diseases usually involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Common medications used to treat these diseases include:
- Beta blockers to lower blood pressure and heart rate
- Statins to lower cholesterol levels
- Antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors to lower blood pressure
- Diuretics to reduce fluid buildup in the body
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a heart-healthy diet can help manage the condition.
Emergency Response to Heart and Brain Vascular Diseases
If someone experiences symptoms of a heart attack or stroke, it is essential to act quickly and seek medical attention immediately. Here are some emergency response measures:
- Call the emergency services number (such as 911 in the US) or get someone to drive the person to the hospital
- If the person is unconscious, not breathing, or does not have a pulse, start CPR if trained to do so
- If the person is experiencing symptoms of a stroke, such as numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, or difficulty speaking, act F.A.S.T. (Face, Arm, Speech, Time)
- Stay with the person until medical help arrives
Daily Life Considerations for Heart and Brain Vascular Disease Patients
Living with heart and brain vascular diseases requires careful attention to daily habits and lifestyle choices. Here are some essential considerations for patients to manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications:
Diet and Nutrition
- Eat a heart-healthy diet: Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products.
- Limit sodium intake: Aim for less than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day to help manage blood pressure.
- Choose healthy fats: Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, to support heart health.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to help maintain blood flow and overall health.
Physical Activity
- Aim for regular exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Incorporate strength training: Include exercises that strengthen muscles, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, at least two times per week.
- Take regular breaks: If you have a desk job, take short breaks to stand up, stretch, and move around every 30-60 minutes.
Stress Management
- Practice relaxation techniques: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, to help manage stress and anxiety.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate stress hormones and support overall health.
- Stay connected: Build and maintain social connections with friends and family to help manage stress and emotional well-being.
Medication Adherence
- Take medications as prescribed: Adhere to your medication regimen as directed by your healthcare provider to manage your condition.
- Monitor side effects: Report any side effects or concerns to your healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Regular Check-Ups
- Schedule regular appointments: Visit your healthcare provider regularly to monitor your condition, adjust medications, and address any concerns.
- Track your health metrics: Keep track of your blood pressure, blood glucose, and lipid profiles to monitor your progress and make informed decisions.
Conclusion
Heart and brain vascular diseases are serious conditions that require attention and action. By understanding the causes, prevention strategies, treatment options, and emergency response measures, we can reduce the risk of these diseases and improve overall health outcomes.
